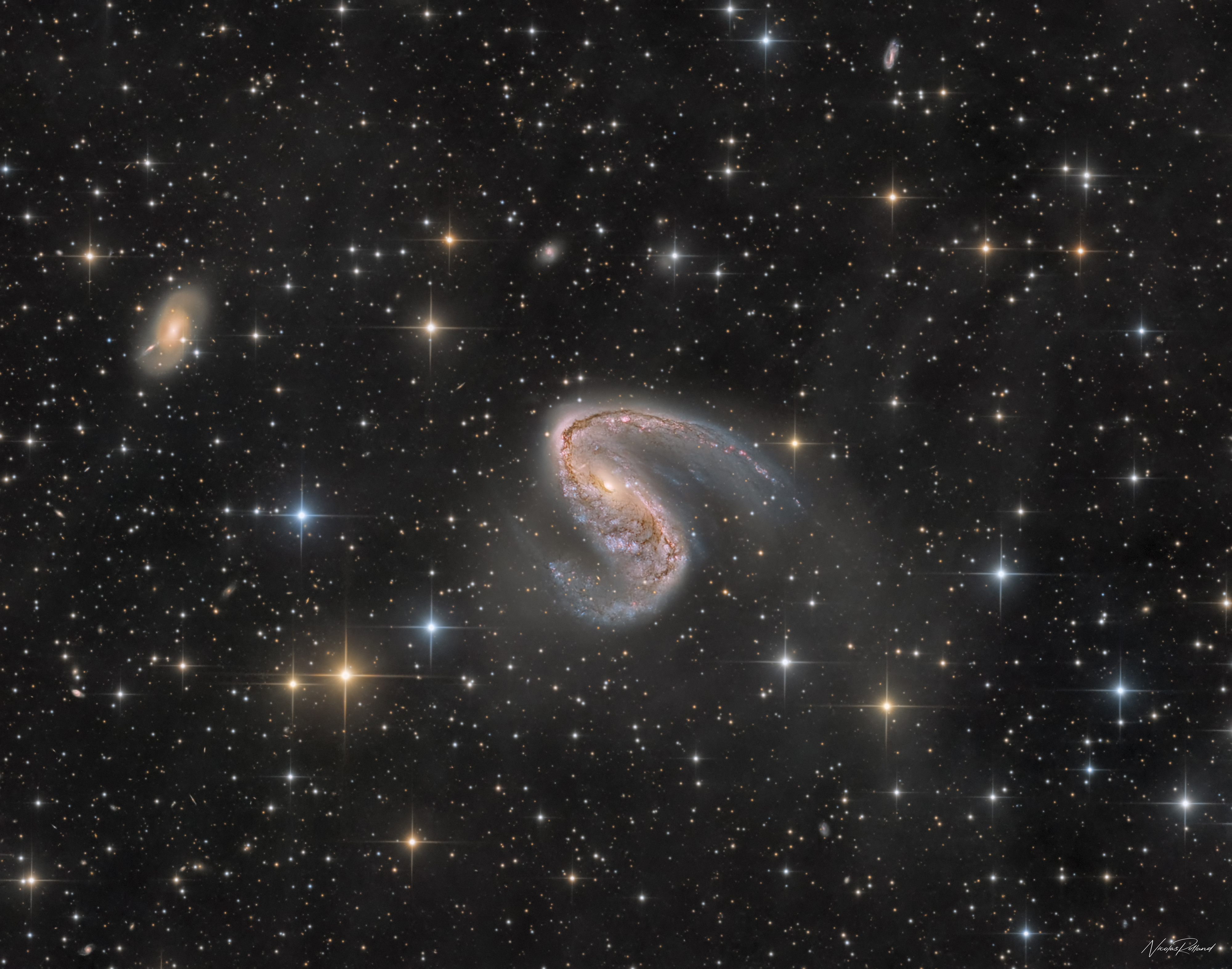
The Meathook Galaxy
NGC 2442
Note: This picture has been selected as NASA's Astronomy Picture of the Day (APOD) on 2023 April 1.
NGC 2442, also known as the Meathook Galaxy, is a barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation of Volans, which lies approximately 75 million light years away from Earth. The galaxy was first discovered by John Herschel, a British astronomer, in 1834 during his observations of the southern sky from South Africa. NGC 2442 is considered to be one of the most visually striking galaxies in the southern hemisphere and has been the subject of extensive study by astronomers for many years.
NGC 2442 has a distinct S-shaped appearance, with two prominent arms extending outwards from the central bar of the galaxy. The arms are littered with numerous bright pink regions of star formation, indicating that NGC 2442 is a site of active star formation.
One of the most striking features of NGC 2442 is the large dust lane that runs through the center of the galaxy, giving it the appearance of a meat hook. The dust lane is thought to be the result of a collision between NGC 2442 and a smaller companion galaxy, which occurred about 200 million years ago. The collision caused gas and dust to be compressed in the central region of the galaxy, triggering a burst of star formation and the formation of the dust lane.
NGC 2442 has a relatively small central bulge compared to other spiral galaxies, and its spiral arms are very tightly wound, which gives the galaxy a very compact appearance. The galaxy’s bar is also quite short and stubby, which is unusual for a galaxy of this type. NGC 2442 has a total mass of approximately 10 billion solar masses, and its diameter is estimated to be around 90,000 light years.
Note: Cette image a été sélectionnée par la NASA's « Astronomical Picture Of the Day » (APOD) le 1er avril 2023.
NGC 2442, également connue sous le nom de galaxie du Crochet de Boucher, est une galaxie spirale barrée située dans la constellation du Poisson volant, à environ 75 millions d'années-lumière de la Terre. La galaxie a été découverte par John Herschel, un astronome britannique, en 1834 lors de ses observations du ciel austral depuis l'Afrique du Sud. NGC 2442 est considérée comme l'une des galaxies les plus connue de l'hémisphère sud et fait l'objet d'une étude approfondie par les astronomes depuis de nombreuses années.
NGC 2442 a une apparence distincte en forme de "S", avec deux bras proéminents s'étendant vers l'extérieur à partir de la barre centrale de la galaxie. Les bras sont parsemés de nombreuses régions rose/rouge vif de formation d'étoiles, ce qui indique que NGC 2442 est une zone de formation active d'étoiles.
L'une des caractéristiques les plus frappantes de NGC 2442 est le large couloir de poussière qui traverse le centre de la galaxie, lui donnant l'apparence d'un crochet de boucher. On pense que ce couloir de poussière est le résultat d'une collision entre NGC 2442 et une galaxie compagnon plus petite, qui s'est produite il y a environ 200 millions d'années. La collision a provoqué la compression du gaz et de la poussière dans la région centrale de la galaxie, déclenchant une explosion de formation d'étoiles et la création du couloir de poussière.
NGC 2442 présente un renflement central relativement petit par rapport aux autres galaxies spirales, et ses bras spiraux sont très serrés, ce qui donne à la galaxie un aspect très compact. La barre de la galaxie est également assez courte et tronquée, ce qui est inhabituel pour une galaxie de ce type. NGC 2442 a une masse totale d'environ 10 milliards de masses solaires, et son diamètre est estimé à environ 90 000 années-lumière.
TECHNICAL DATA
ACQUISITION DETAILS
OPTICS Planewave CDK17 @ F/6.8
CAMERA SBIG STXL-11002 (AOX)
MOUNT Paramount ME
FILTERS Ha, L, R, G, B
LOCATION El Sauce Pbservatory, Rio Hurtado, Chile
DATE December 2022 & January 2020
EXPOSURES 48 hours (Ha: 9*1800sec, L: 38*1200sec, R: 21*900sec + 15*1200sec, G: 21*900sec + 15*1200sec, B: 20*900sec + 16*1200sec)
PROCESSING SOFTWARE Pixinsight, Photoshop
COPYRIGHTS Martin Pugh & Nicolas Rolland
TARGET DETAILS
RA 07h 36m 21.8s
DEC -69° 31' 48.8"
SIZE 26.8 x 21.1 arcmin
ORIENTATION Up is 359 degrees E of N
CONSTELLATION Vollans
DISTANCE 75 million ly
MAGNITUDE 10.5
